Différences entre les versions de « ERG::physicalcomputing »
Aller à la navigation
Aller à la recherche
| Ligne 26 : | Ligne 26 : | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
| − | + | ||
* This sketch shows how to use the FFT class to analyze a stream | * This sketch shows how to use the FFT class to analyze a stream | ||
* of sound. Change the number of bands to get more spectral bands | * of sound. Change the number of bands to get more spectral bands | ||
| Ligne 76 : | Ligne 76 : | ||
public void draw() { | public void draw() { | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
// Perform the analysis | // Perform the analysis | ||
fft.analyze(); | fft.analyze(); | ||
| − | + | int currentBand = 0; | |
| + | float maxVal = 0; | ||
| + | |||
for (int i = 0; i < bands; i++) { | for (int i = 0; i < bands; i++) { | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | if(fft.spectrum[i] > maxVal){ | |
| − | + | currentBand = i; | |
| − | + | maxVal = fft.spectrum[i]; | |
| − | + | } | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | if(currentBand > 10){ | ||
| + | background(0); | ||
| + | }else{ | ||
| + | background(255); | ||
} | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
} | } | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Version du 22 octobre 2018 à 09:28
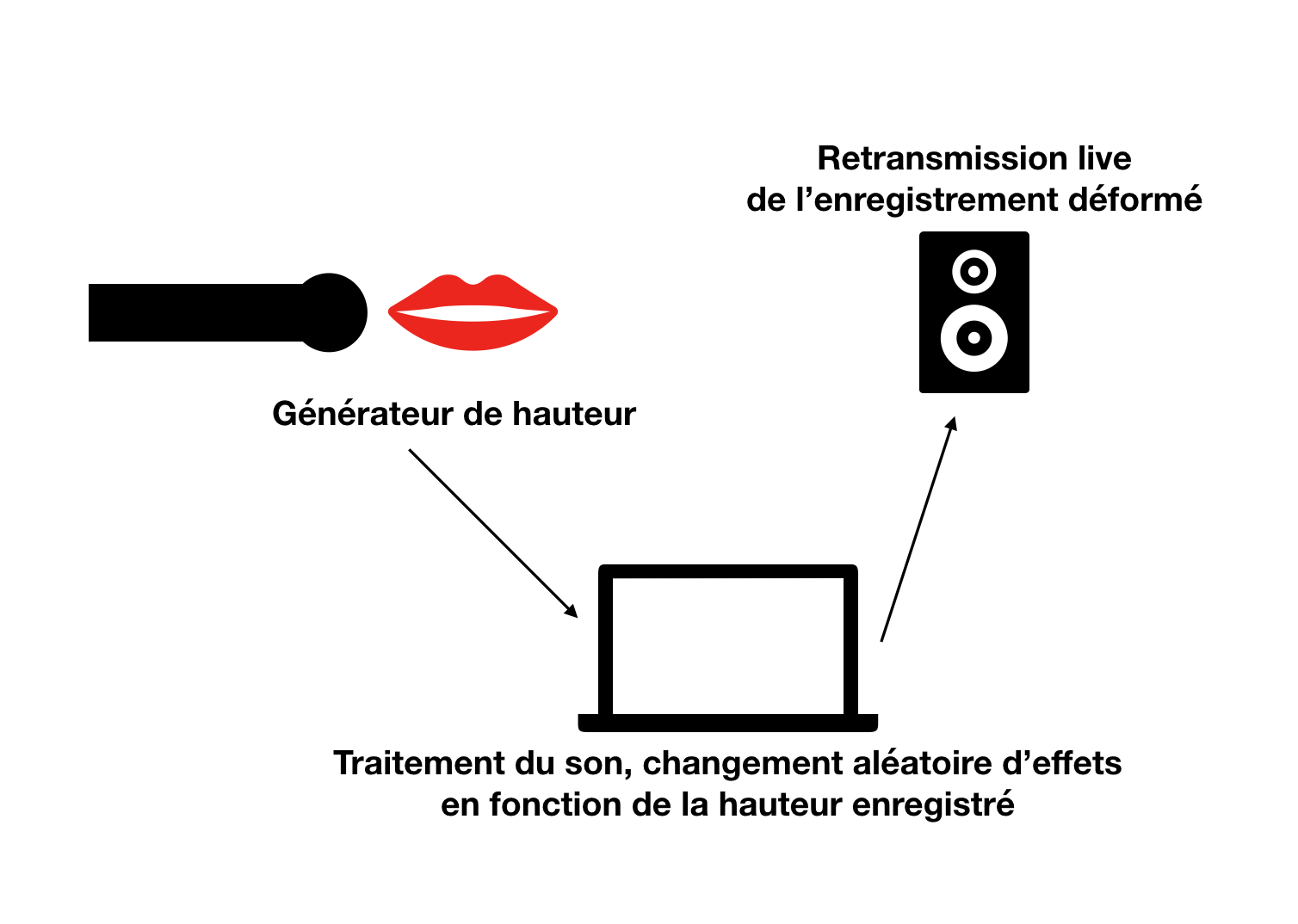
projet : Assigner un programme différent à chaque octave de la voix. Donc avec un système de détection des notes et des hauteurs. Chacune des notes seraient assignée à un effet de type stéréo, réverbe, granulator...
Utilisation de processing.
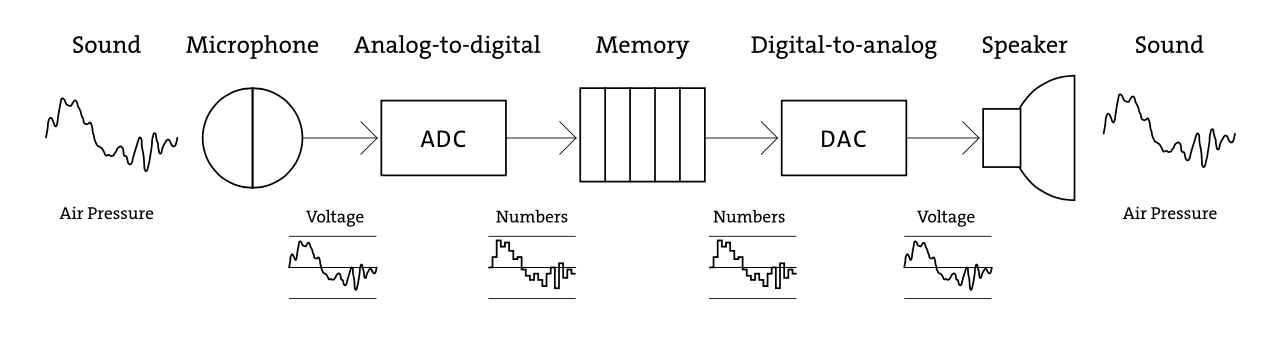
- Réaliser du code qui récupère les données enregistrées par un Micro externe, analyser ces données.
Exo 1 : traduire par une couleur des paliers sur la hauteur du son enregistré.
Code utilisé : Modifications réalisées sur le code : -FFT à partir d'un enregistrement micro input -Retour Micro
ATTENTION UTILISER CASQUE AUDIO SINON LARSEN
* This sketch shows how to use the FFT class to analyze a stream
* of sound. Change the number of bands to get more spectral bands
* (at the expense of more coarse-grained time resolution of the spectrum).
*/
import processing.sound.*;
// Declare the sound source and FFT analyzer variables
FFT fft;
AudioIn in;
// Define how many FFT bands to use (this needs to be a power of two)
int bands = 128;
// Define a smoothing factor which determines how much the spectrums of consecutive
// points in time should be combined to create a smoother visualisation of the spectrum.
// A smoothing factor of 1.0 means no smoothing (only the data from the newest analysis
// is rendered), decrease the factor down towards 0.0 to have the visualisation update
// more slowly, which is easier on the eye.
float smoothingFactor = 0.2;
// Create a vector to store the smoothed spectrum data in
float[] sum = new float[bands];
// Variables for drawing the spectrum:
// Declare a scaling factor for adjusting the height of the rectangles
int scale = 5;
// Declare a drawing variable for calculating the width of the
float barWidth;
public void setup() {
size(640, 360);
background(255);
// Calculate the width of the rects depending on how many bands we have
barWidth = width/float(bands);
// Load and play a soundfile and loop it.
fft = new FFT(this, bands);
in = new AudioIn(this, 0);
// Create the FFT analyzer and connect the playing soundfile to it.
in.start();
fft.input(in);
//retour micro
in.play();
}
public void draw() {
// Perform the analysis
fft.analyze();
int currentBand = 0;
float maxVal = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < bands; i++) {
if(fft.spectrum[i] > maxVal){
currentBand = i;
maxVal = fft.spectrum[i];
}
}
if(currentBand > 10){
background(0);
}else{
background(255);
}
}