Différences entre les versions de « ERG::physicalcomputing »
Aller à la navigation
Aller à la recherche
| Ligne 16 : | Ligne 16 : | ||
'''EXEMPLE DE CODE À COMPRENDRE ET REUTILISER :''' | '''EXEMPLE DE CODE À COMPRENDRE ET REUTILISER :''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * Grab audio from the microphone input and draw a circle whose size | ||
| + | * is determined by how loud the audio input is. | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | |||
| + | import processing.sound.*; | ||
| + | |||
| + | AudioIn input; | ||
| + | Amplitude loudness; | ||
| + | |||
| + | void setup() { | ||
| + | size(640, 360); | ||
| + | background(255); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Create an Audio input and grab the 1st channel | ||
| + | input = new AudioIn(this, 0); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Begin capturing the audio input | ||
| + | input.start(); | ||
| + | // start() activates audio capture so that you can use it as | ||
| + | // the input to live sound analysis, but it does NOT cause the | ||
| + | // captured audio to be played back to you. if you also want the | ||
| + | // microphone input to be played back to you, call | ||
| + | // input.play(); | ||
| + | // instead (be careful with your speaker volume, you might produce | ||
| + | // painful audio feedback. best to first try it out wearing headphones!) | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Create a new Amplitude analyzer | ||
| + | loudness = new Amplitude(this); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Patch the input to the volume analyzer | ||
| + | loudness.input(input); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | void draw() { | ||
| + | // Adjust the volume of the audio input based on mouse position | ||
| + | float inputLevel = map(mouseY, 0, height, 1.0, 0.0); | ||
| + | input.amp(inputLevel); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // loudness.analyze() return a value between 0 and 1. To adjust | ||
| + | // the scaling and mapping of an ellipse we scale from 0 to 0.5 | ||
| + | float volume = loudness.analyze(); | ||
| + | int size = int(map(volume, 0, 0.5, 1, 350)); | ||
| + | |||
| + | background(125, 255, 125); | ||
| + | noStroke(); | ||
| + | fill(255, 0, 150); | ||
| + | // We draw a circle whose size is coupled to the audio analysis | ||
| + | ellipse(width/2, height/2, size, size); | ||
| + | } | ||
Version du 15 octobre 2018 à 07:06
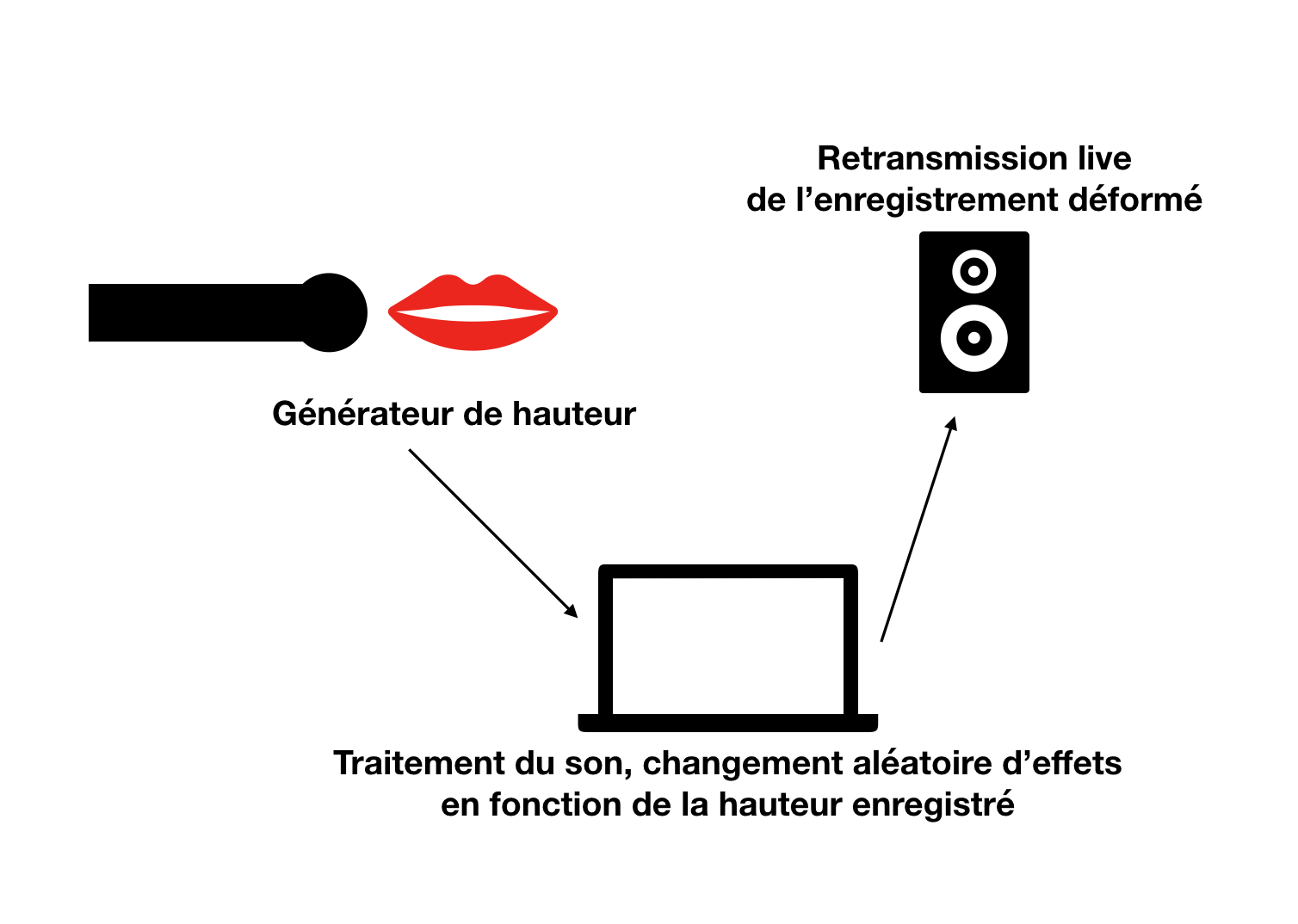
projet : Assigner un programme différent à chaque octave de la voix. Donc avec un système de détection des notes et des hauteurs. Chacune des notes seraient assignée à un effet de type stéréo, réverbe, granulator...
Utilisation de processing.
- Réaliser du code qui récupère les données enregistrées par un Micro externe, analyser ces données.
Exo 1 : traduire par une couleur des paliers sur la hauteur du son enregistré.
EXEMPLE DE CODE À COMPRENDRE ET REUTILISER :
/**
* Grab audio from the microphone input and draw a circle whose size * is determined by how loud the audio input is. */
import processing.sound.*;
AudioIn input; Amplitude loudness;
void setup() {
size(640, 360); background(255);
// Create an Audio input and grab the 1st channel input = new AudioIn(this, 0);
// Begin capturing the audio input input.start(); // start() activates audio capture so that you can use it as // the input to live sound analysis, but it does NOT cause the // captured audio to be played back to you. if you also want the // microphone input to be played back to you, call // input.play(); // instead (be careful with your speaker volume, you might produce // painful audio feedback. best to first try it out wearing headphones!)
// Create a new Amplitude analyzer loudness = new Amplitude(this);
// Patch the input to the volume analyzer loudness.input(input);
}
void draw() {
// Adjust the volume of the audio input based on mouse position float inputLevel = map(mouseY, 0, height, 1.0, 0.0); input.amp(inputLevel);
// loudness.analyze() return a value between 0 and 1. To adjust // the scaling and mapping of an ellipse we scale from 0 to 0.5 float volume = loudness.analyze(); int size = int(map(volume, 0, 0.5, 1, 350));
background(125, 255, 125); noStroke(); fill(255, 0, 150); // We draw a circle whose size is coupled to the audio analysis ellipse(width/2, height/2, size, size);
}